@Observed装饰器和@ObjectLink装饰器:嵌套类对象属性变化
上文所述的装饰器仅能观察到第一层的变化,但是在实际应用开发中,应用会根据开发需要,封装自己的数据模型。对于多层嵌套的情况,比如二维数组,或者数组项class,或者class的属性是class,他们的第二层的属性变化是无法观察到的。这就引出了@Observed/@ObjectLink装饰器。
从API version 9开始,这两个装饰器支持在ArkTS卡片中使用。
概述
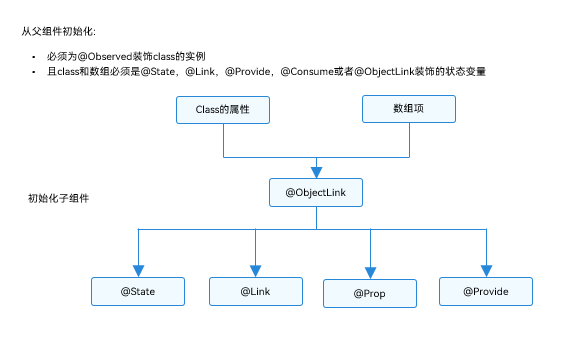
@ObjectLink和@Observed类装饰器用于在涉及嵌套对象或数组的场景中进行双向数据同步:
- 被@Observed装饰的类,可以被观察到属性的变化;
- 子组件中@ObjectLink装饰器装饰的状态变量用于接收@Observed装饰的类的实例,和父组件中对应的状态变量建立双向数据绑定。这个实例可以是数组中的被@Observed装饰的项,或者是class object中的属性,这个属性同样也需要被@Observed装饰。
- 单独使用@Observed是没有任何作用的,需要搭配@ObjectLink或者@Prop使用。
限制条件
- 使用@Observed装饰class会改变class原始的原型链,@Observed和其他类装饰器装饰同一个class可能会带来问题。
- @ObjectLink装饰器不能在@Entry装饰的自定义组件中使用。
装饰器说明
@Observed类装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
装饰器参数 | 无 |
类装饰器 | 装饰class。需要放在class的定义前,使用new创建类对象。 |
@ObjectLink变量装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
装饰器参数 | 无 |
同步类型 | 不与父组件中的任何类型同步变量。 |
允许装饰的变量类型 | 必须为被@Observed装饰的class实例,必须指定类型。 不支持简单类型,可以使用@Prop。 @ObjectLink的属性是可以改变的,但是变量的分配是不允许的,也就是说这个装饰器装饰变量是只读的,不能被改变。 |
被装饰变量的初始值 | 不允许。 |
@ObjectLink装饰的数据为可读示例。
- // 允许@ObjectLink装饰的数据属性赋值
- this.objLink.a= ...
- // 不允许@ObjectLink装饰的数据自身赋值
- this.objLink= ...
@ObjectLink装饰的变量不能被赋值,如果要使用赋值操作,请使用@Prop。
- @Prop装饰的变量和数据源的关系是是单向同步,@Prop装饰的变量在本地拷贝了数据源,所以它允许本地更改,如果父组件中的数据源有更新,@Prop装饰的变量本地的修改将被覆盖;
- @ObjectLink装饰的变量和数据源的关系是双向同步,@ObjectLink装饰的变量相当于指向数据源的指针。如果一旦发生@ObjectLink装饰的变量的赋值,则同步链将被打断。
观察的变化
@Observed装饰的类,如果其属性为非简单类型,比如class、Object或者数组,也需要被@Observed装饰,否则将观察不到其属性的变化。
- class ClassA {
- public c: number;
- constructor(c: number) {
- this.c = c;
- }
- }
- @Observed
- class ClassB {
- public a: ClassA;
- public b: number;
- constructor(a: ClassA, b: number) {
- this.a = a;
- this.b = b;
- }
- }
以上示例中,ClassB被@Observed装饰,其成员变量的赋值的变化是可以被观察到的,但对于ClassA,没有被@Observed装饰,其属性的修改不能被观察到。
- @ObjectLink b: ClassB
- // 赋值变化可以被观察到
- this.b.a = new ClassA(5)
- this.b.b = 5
- // ClassA没有被@Observed装饰,其属性的变化观察不到
- this.b.a.c = 5
@ObjectLink:@ObjectLink只能接收被@Observed装饰class的实例,可以观察到:
- 其属性的数值的变化,其中属性是指Object.keys(observedObject)返回的所有属性,示例请参考嵌套对象。
- 如果数据源是数组,则可以观察到数组item的替换,如果数据源是class,可观察到class的属性的变化,示例请参考对象数组。
框架行为
- 初始渲染:
- @Observed装饰的class的实例会被不透明的代理对象包装,代理了class上的属性的setter和getter方法
- 子组件中@ObjectLink装饰的从父组件初始化,接收被@Observed装饰的class的实例,@ObjectLink的包装类会将自己注册给@Observed class。
- 属性更新:当@Observed装饰的class属性改变时,会走到代理的setter和getter,然后遍历依赖它的@ObjectLink包装类,通知数据更新。
嵌套对象
以下是嵌套类对象的数据结构。
- // objectLinkNestedObjects.ets
- let NextID: number = 1;
- @Observed
- class ClassA {
- public id: number;
- public c: number;
- constructor(c: number) {
- this.id = NextID++;
- this.c = c;
- }
- }
- @Observed
- class ClassB {
- public a: ClassA;
- constructor(a: ClassA) {
- this.a = a;
- }
- }
- @Component
- struct ViewA {
- label: string = 'ViewA1';
- @ObjectLink a: ClassA;
- build() {
- Row() {
- Button(`ViewA [${this.label}] this.a.c=${this.a.c} +1`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.a.c += 1;
- })
- }
- }
- }
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct ViewB {
- @State b: ClassB = new ClassB(new ClassA(0));
- build() {
- Column() {
- // in low version,DevEco may throw a warning,but it does not matter.
- // you can still compile and run.
- ViewA({ label: 'ViewA #1', a: this.b.a })
- ViewA({ label: 'ViewA #2', a: this.b.a })
- Button(`ViewB: this.b.a.c+= 1`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.b.a.c += 1;
- })
- Button(`ViewB: this.b.a = new ClassA(0)`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.b.a = new ClassA(0);
- })
- Button(`ViewB: this.b = new ClassB(ClassA(0))`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.b = new ClassB(new ClassA(0));
- })
- }
- }
- }
ViewB中的事件句柄:
- this.b.a = new ClassA(0) 和this.b = new ClassB(new ClassA(0)): 对@State装饰的变量b和其属性的修改。
- this.b.a.c = ... :该变化属于第二层的变化,@State无法观察到第二层的变化,但是ClassA被@Observed装饰,ClassA的属性c的变化可以被@ObjectLink观察到。
ViewA中的事件句柄:
- this.a.c += 1:对@ObjectLink变量a的修改,将触发Button组件的刷新。@ObjectLink和@Prop不同,@ObjectLink不拷贝来自父组件的数据源,而是在本地构建了指向其数据源的引用。
- @ObjectLink变量是只读的,this.a = new ClassA(...)是不允许的,因为一旦赋值操作发生,指向数据源的引用将被重置,同步将被打断。
对象数组
对象数组是一种常用的数据结构。以下示例展示了数组对象的用法。
- @Component
- struct ViewA {
- // 子组件ViewA的@ObjectLink的类型是ClassA
- @ObjectLink a: ClassA;
- label: string = 'ViewA1';
- build() {
- Row() {
- Button(`ViewA [${this.label}] this.a.c = ${this.a.c} +1`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.a.c += 1;
- })
- }
- }
- }
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct ViewB {
- // ViewB中有@State装饰的ClassA[]
- @State arrA: ClassA[] = [new ClassA(0), new ClassA(0)];
- build() {
- Column() {
- ForEach(this.arrA,
- (item) => {
- ViewA({ label: `#${item.id}`, a: item })
- },
- (item) => item.id.toString()
- )
- // 使用@State装饰的数组的数组项初始化@ObjectLink,其中数组项是被@Observed装饰的ClassA的实例
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[first]`, a: this.arrA[0] })
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[last]`, a: this.arrA[this.arrA.length-1] })
- Button(`ViewB: reset array`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA = [new ClassA(0), new ClassA(0)];
- })
- Button(`ViewB: push`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA.push(new ClassA(0))
- })
- Button(`ViewB: shift`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA.shift()
- })
- Button(`ViewB: chg item property in middle`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length / 2)].c = 10;
- })
- Button(`ViewB: chg item property in middle`)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length / 2)] = new ClassA(11);
- })
- }
- }
- }
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length/2)] = new ClassA(..) :该状态变量的改变触发2次更新:
- ForEach:数组项的赋值导致ForEach的itemGenerator被修改,因此数组项被识别为有更改,ForEach的item builder将执行,创建新的ViewA组件实例。
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[last]`, a: this.arrA[this.arrA.length-1] }):上述更改改变了数组中第二个元素,所以绑定this.arrA[1]的ViewA将被更新;
- this.arrA.push(new ClassA(0)) : 将触发2次不同效果的更新:
- ForEach:新添加的ClassA对象对于ForEach是未知的itemGenerator,ForEach的item builder将执行,创建新的ViewA组件实例。
- ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[last]`, a: this.arrA[this.arrA.length-1] }):数组的最后一项有更改,因此引起第二个ViewA的实例的更改。对于ViewA({ label: `ViewA this.arrA[first]`, a: this.arrA[0] }),数组的更改并没有触发一个数组项更改的改变,所以第一个ViewA不会刷新。
- this.arrA[Math.floor(this.arrA.length/2)].c:@State无法观察到第二层的变化,但是ClassA被@Observed装饰,ClassA的属性的变化将被@ObjectLink观察到。
二维数组
使用@Observed观察二维数组的变化。可以声明一个被@Observed装饰的继承Array的子类。
- @Observed
- class StringArray extends Array<String> {
- }
使用new StringArray()来构造StringArray的实例,new运算符使得@Observed生效,@Observed观察到StringArray的属性变化。
声明一个从Array扩展的类class StringArray extends Array<String> {},并创建StringArray的实例。@Observed装饰的类需要使用new运算符来构建class实例。
- @Observed
- class StringArray extends Array<String> {
- }
- @Component
- struct ItemPage {
- @ObjectLink itemArr: StringArray;
- build() {
- Row() {
- Text('ItemPage')
- .width(100).height(100)
- ForEach(this.itemArr,
- item => {
- Text(item)
- .width(100).height(100)
- },
- item => item
- )
- }
- }
- }
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct IndexPage {
- @State arr: Array<StringArray> = [new StringArray(), new StringArray(), new StringArray()];
- build() {
- Column() {
- ItemPage({ itemArr: this.arr[0] })
- ItemPage({ itemArr: this.arr[1] })
- ItemPage({ itemArr: this.arr[2] })
- Divider()
- ForEach(this.arr,
- itemArr => {
- ItemPage({ itemArr: itemArr })
- },
- itemArr => itemArr[0]
- )
- Divider()
- Button('update')
- .onClick(() => {
- console.error('Update all items in arr');
- if (this.arr[0][0] !== undefined) {
- // 正常情况下需要有一个真实的ID来与ForEach一起使用,但此处没有
- // 因此需要确保推送的字符串是唯一的。
- this.arr[0].push(`${this.arr[0].slice(-1).pop()}${this.arr[0].slice(-1).pop()}`);
- this.arr[1].push(`${this.arr[1].slice(-1).pop()}${this.arr[1].slice(-1).pop()}`);
- this.arr[2].push(`${this.arr[2].slice(-1).pop()}${this.arr[2].slice(-1).pop()}`);
- } else {
- this.arr[0].push('Hello');
- this.arr[1].push('World');
- this.arr[2].push('!');
- }
- })
- }
- }
- }

 免费AI编程助手
免费AI编程助手




更多建议: